Water Services
Boart Longyear offers a full range of mine and other water services drilling. This includes production, de-watering, re-injection, monitoring, geothermal, and municipal wells.
• Unique process which is capable of drilling large diameter holes in a single pass
• Better overall well efficiency and production
• Helps eliminate downtime and money spent over the life of the well
Methods
Dual Tube Flooded Reverse
Dual Tube Flooded Reverse – The drilling process using dual wall drill pipe and drilling fluid along with the injection of air to drill large diameter holes. In the drill sting there are perforations that allow the air to return up the center following the path of least resistance. The air traveling back up the inner tube creates a vacuum which in turn sucks up the cuttings from the bottom of the hole at the face of the bit.In the DTFR system fluids always circulate inside the dual tube pipe and can’t escape into the formations. Instead of maintaining fluids at the surface and circulating throughout the wellbore the DTFR system will generally drill with the borehole fluids at their naturally occurring level. Boart uses the DTFR system to effectively drill large diameter water wells around the globe.
Conventional Air
Direct Air Rotary drilling forces compressed air down the drill string and through holes in the bit. The compressed air collects the cuttings, and carries them to the surface. This method is often used in softer formations ≠Air Hammer Drilling forces compressed air through the drill pipe to drive an air hammer bit at the bottom of the borehole. The pneumatic bit rapidly strikes the rock, pulverizing it. The entire drill string is simultaneously rotated during drilling to aid in keeping the borehole straight. After the compressed air exits the hammer, cuttings are collected to the surface. This method advances quickly, even in hard formations.
Air Hammer Drilling forces compressed air through the drill pipe to drive an air hammer bit at the bottom of the borehole. The pneumatic bit rapidly strikes the rock, pulverizing it. The entire drill string is simultaneously rotated during drilling to aid in keeping the borehole straight. After the compressed air exits the hammer, cuttings are collected to the surface. This method advances quickly, even in hard formations.
Air drilling doesn’t seal off the borehole, which allows for higher producing aquifers than mud rotary.
Conventional Mud
Mud rotary utilizes drilling fluid (mud) to cool down the drill bit and simultaneously remove cuttings from the bottom of the borehole. Drilling mud can consists of various ingredients, the most common being bentonite and polymers. As the mud returns to the surface it is collected in a mud tank where the cuttings settle and the mud is reused in the drilling process. This method is commonly used in sand and gravel formations where borehole wall stability is an issue. The drilling mud helps to stabilize the borehole.
Dual Rotary
Dual Rotary maintains borehole stability by advancing an outer casing, which allows advancement in the most challenging ground conditions where other overburden drilling systems are unsuccessful. Once the casing is in place, hole is advanced to desired depth into a competent geological formation and well installation can be accomplished in a controlled environment.
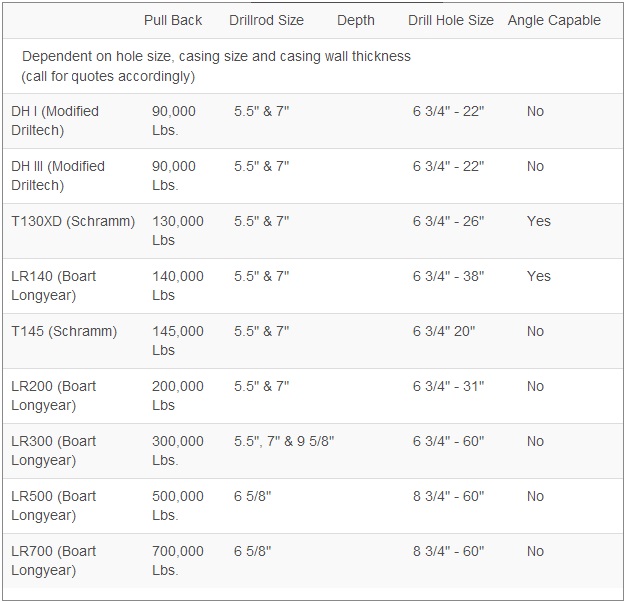
Fleet
Expertise
Dewatering
The process of moving water from an aquifer by pumping water out of the well or by vertical and horizontal drains. Boart Longyear has drilled numerous wells with multiple size completions globally to help mines dewater in order to maintain the stability of the open pit or underground mine. The wells are completed in Alluvial, over burden and hard rock formations. Boart has various size rigs that have capabilities to drill wells up to 60” in diameter and depths up to 8,000’ +
Portable Wells
These are wells that are safe enough to be consumed by humans, usually water supplied to households, commerce and industry. Boart has extensive experience drilling potable water wells for municipalities and private water corporations. The drilled wells are larger completions, 12” – 18” and depths of up to 3,000’ +.
Paste Holes
Sometimes referred to as “service holes”. These are holes that are drilled and cased at underground mines. These cased holes are then used to supply utilities, aggregate, cement, air shafts, etc. to the underground mine.
Injection Wells
Wells vertically drilled to pump water, other liquids, or gases into specific geological formations. Boart has been involved with the drilling of injection wells to relocate water from one aquifer to another aquifer as well as drilling wells for the research of CO2 injection. These wells can be large or small diameter wells with depths of up to 8,000’ +.
Angle Wells
Wells drilled at an angle to reach a target that otherwise would not be obtainable. Typically the understanding of angle wells is that they are drilled directionally. Boart uses a unique bottom hole assembly to drill angle water wells to achieve the target desired. Usually the technique is used for smaller diameter completion wells but depending on ground conditions can be used for large completion wells. They are not only used to hit a specific target but also allows the ability to drill through multiple vertical water bearing fractures that if drilled vertically usually produce less gallon per minute.
Depressurizing
Often times there are pockets of water near the walls of a pit that create pressure against the wall making it unstable. We will go in and drill horizontal holes in the wall to create an outlet for water to drain and relieve wall pressure.
Directional Drilling
The process of drilling non vertical wells to hit a specific target. The directional process uses a mud motor to rotate the bit with a unique bottom hole assembly to allow the string to be steered to hit the desired target. These holes are usually drilled with mud conventional but also can be drilled with air conventional to power the mud motor and clean the well. Surveys are taken throughout the drilling process to ensure the hole is on target. Boart uses directional capabilities to drill paste holes, methane vent wells, pre collar for raise bores, water wells and sometimes mineral exploration.
Source: http://www.boartlongyear.com/drilling-services/water-services/

|
Boart Longyear is accepting resumes for the role of Stockroom Labourer based in North Bay, Ontario.
Boart Longyear is accepting resumes for the role of a Maintenance Supervisor in our North Bay, Ontario Manufacturing facility.
Heavy-duty equipment mechanics repair, troubleshoot, adjust, overhaul and maintain heavy duty mobile drilling equipment and mobile support equipment used within the scope of Boart Longyear Drilling operations.