Rubicon Minerals Corp.
Phoenix Gold Project
Key Facts and Technical Report
Location: Red Lake, Ontario, Canada
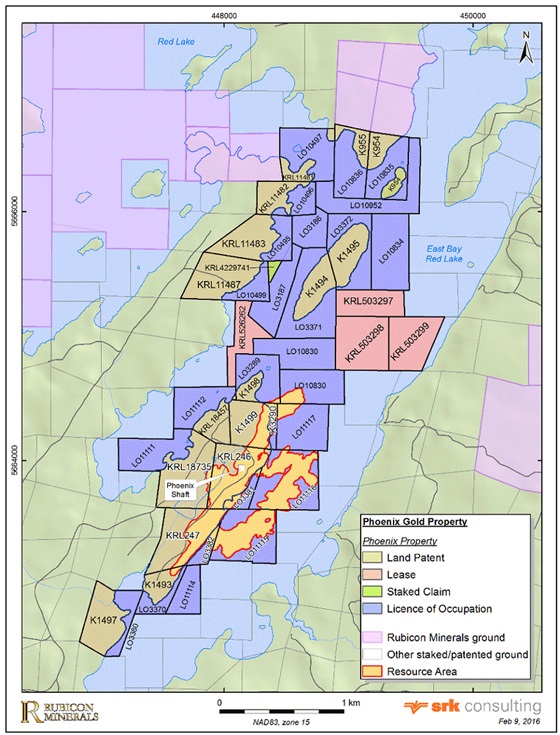
Mineral Tenure: 510.4 ha (Phoenix Gold Property)
Interest: 100% mineral rights
Deposit type: High-grade Archean lode gold (underground)
Stage: Project Development
Infrastructure: 1,800 tpd mill circuit (permitted for 1,250 tpd), +14 km U/G development, shaft
Royalties: 3.0% (Franco Nevada 2.0% on water claims; Royal Gold 1.0% on land claims)
Introduction
The Phoenix Gold Project is an underground exploration project located in the district of Red Lake, Ontario, Canada. It is located approximately 265 kilometres (km) northeast of Winnipeg, Manitoba. Rubicon wholly owns 100 percent (%) of the Phoenix Gold Project. The Phoenix Gold Project consists of the high-grade F2 Gold Deposit, more than 9,000 m of underground development including a commissioned shaft that goes down approximately 730 m below surface, and surface infrastructure that includes a 1,250 tonne per day mill facility (currently in care and maintenance), a completed tailings management facility, electric power supply and substation, 200-person camp, earth-works and civil-works.
History and Current Status
The exploration and mining history of the Red Lake mining district dates back to 1925, when significant gold was first discovered by prospector L. B. Howey. The Phoenix gold property (previously known as the McFinley property) was initially staked and owned by McCallum Red Lake Mines Ltd. in 1922. After a series of ownership changes, Rubicon optioned the property from Dominion Goldfields Corporation in two agreements in 2002. The surface rights of the Patented Claims are now owned by 0691403 B.C. Ltd., a wholly owned subsidiary of Rubicon.
Since acquiring the Phoenix gold project in 2002, Rubicon has conducted an extensive exploration program, which includes geological mapping, re-logging of selected historic boreholes, digital compilation of available historical data, ground and airborne magnetic surveys, mechanical trenching, channel sampling, bathymetric survey, airborne high resolution resistivity and induced polarization (DCIP), Titan 24 geophysical survey, petrographic study, topographic survey, data modelling and processing, along with numerous drilling programs. Since 2002 and up to November 1, 2015, Rubicon has completed 523,283 m of core drilling (235,228 m from the surface and 288,055 m from underground stations) on the Phoenix gold project. During this period, 450,175 m of drilling targeted the F2 gold system. Since October 31, 2012, 561 new core boreholes (94,575 m) have been drilled with the majority of the new boreholes consisting of infill drilling targeting the Main Zone of the F2 Gold Deposit from underground drilling stations.
Since the end of 2016, here are major milestones achieved at the Phoenix Gold Project:
- REPUTABLE CONSULTANTS: Golder Associates and T. Maunula & Associates have been working with Rubicon since early 2017.
- NEW STRUCTURAL MODEL SHOWS BETTER CONTINUITY : Simplified interpretation allows for the evaluation of bulk mining methods
- 2018 MINERAL RESOURCE ESTIMATE DEMONSTRATED SIGNIFICANT GROWTH: M&I Resources increased +113%; Inferred Resources increased +81%
- POSITIVE 35K-TONNE BULK SAMPLE RECONCILIATION: Validating 2018 Mineral Resource Estimate and new geological model
- +110% INCREASE IN 2019 MEASURED & INDICATED RESOURCES: 2019 Mineral Resource Estimate demonstrated substantial growth in ounces in higher confidence categories
Location
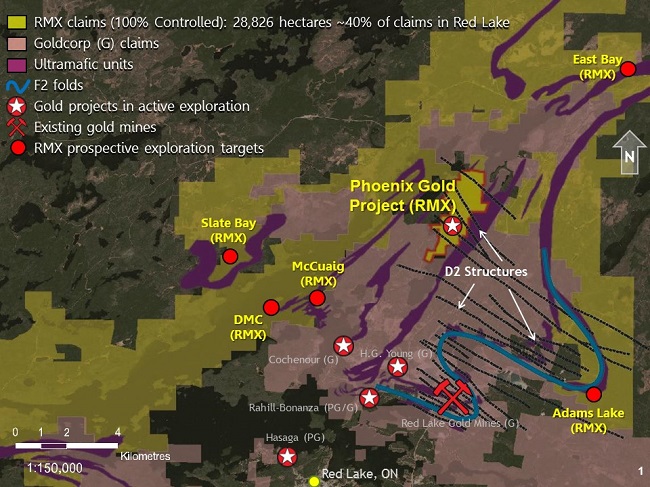
The Phoenix gold project is located in the southwestern part of Bateman Township within the Red Lake mining district of northwestern Ontario, Canada (Figure 1). The town of Red Lake is approximately 150 kilometres (km) northwest of Dryden, Ontario and 265 km northeast of Winnipeg, Manitoba. The total area of the mineral tenure is 510.4 hectares. The Phoenix gold project is centred on the historical McFinley Shaft (now called the Phoenix Shaft), located at latitude 51.13 degrees north and longitude 93.74 degrees west. Rubicon has a 100 percent (%) interest in the Phoenix Gold Project.
Geology
The Phoenix Gold Project is located in the Red Lake Greenstone Belt, of the Superior Province of the Canadian Precambrian Shield, one of Canada’s preeminent gold producing districts with more than 26 million ounces of gold produced since the 1930s. The Red Lake Greenstone Belt is subdivided into several rock assemblages recording magmatic and sedimentary activities that occurred from 3.0 to 2.7 billion years before the present. The tholeiitic and komatiitic metabasalts of the Balmer Assemblage are the oldest volcanic rocks in the greenstone belt and its lower and middle portions host the major lode gold deposits in the Red Lake district. The Phoenix Gold Project is hosted within northeast-trending Balmer Assemblage, which, in this area, is comprised of three tholeiitic mafic volcanic rock sequences, separated by distinct marker horizons of felsic and ultramafic volcanic rock. A strong north-northeast-trending (north-south mine grid) structural fabric pervasive through the area is considered part of the East Bay Deformation Zone. The F2 Gold Deposit occurs in a northeast-trending (north-trending mine grid) sequence of interbedded ultramafic and high-titanium basaltic rocks (HiTi basalt) that is cut by a series of felsic intrusive rock and minor mafic dikes. At least four generations of structures occur in the F2 deposit. The first generation (D1) is associated with a northeast-trending (north-trending mine grid) penetrative foliation (S1) that primarily occurs in ultramafic rock. D2 structures are characterized by east-southeast- and north-northwest-trending (east-northeast- and westnorthwest-trending mine grid) shear zones. The D2 shear zones are typically characterized by less than 1-to 3- metre wide zones of strongly-developed foliation, and occur with or without sets of laminated quartz veins or extensional quartz vein arrays.
Underground development completed since 2013 has exposed the gold mineralization for study and approximately 95,000 metres (m) of new infill core drilling completed since 2013 has helped understand better its relationship to D2 shear zones and its distribution.
While the new geological information confirms the conceptual geological interpretation of 2013, the controls on the distribution of higher grade gold mineralization are now better defined. Gold mineralization in the F2 gold system is characterized by vein and sulphide replacement style mineralization hosted within two main rock types – HiTi basalt units and felsic intrusive rock. These rock types have been correlated over vertical distances of approximately 1,500 m and horizontal distances of approximately 1,200 m. Gold mineralization occurred in two main stages: an early stage overprinted by D1 and a later stage controlled by D2 shear zones. The spatial relationship between D2 shear zones and the second phase of gold mineralization could not be fully appreciated until new underground development excavated in 2014 and 2015 exposed more of the auriferous system.
Source: https://rubiconminerals.com/Exploration-Projects/Phoenix-Gold-Project/default.aspx

|